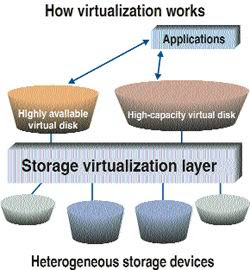
SAN or storage array performance problems can be
identified at the host or backend storage environment.
The diagram below shows a typical performance impact
in the more complex environment.
With SAN
attached storage you can share storage across multiple servers, one of the
downsides of this is that you can have storage response impact across multiple
servers too.
Performance Capacity – Host Metrics
It's important that you understand the limitations of
certain host metrics.
A selection of host metrics are shown below:
•
Measured response is the best metric for identifying
trouble.
•
Host utilization only shows busy time, it doesn’t give
capacity for SAN.
•
Physical IOPs is an important measure of throughput,
all disks have their limitation.
•
Queue Length is a good indicator that a limitation has
been reached somewhere.
Performance Capacity – Host Metrics
Metrics like host utilization can indicate impactful
events, but ample capacity might still be available.
The high utilization can be seen generating
large amounts of I/O in the chart below.
Queue lengths indicate that it may not currently be
impacting response, but headroom is unknown. Response time is the key, as users
will be impacted if it goes up.
On Wednesday
I’ll be taking a look at array architecture.
Dale
Feiste
Principal
Consultant