As mentioned previously the Read/Write metrics can
help you to get a handle on your workload profiles.
Application type is important in estimating
performance risk, for instance, something like Exchange is a heavy I/O user.
I’ve also
seen examples where virtual workstations were being installed and resulted in a
large I/O hit that could have impacted other applications sharing storage.
Scorecards
This is an
example of a score card, where you can have a large amount of information
condensed in to one easy to view dashboard.
Dashboards
I've included an example
below of how you can set up a dashboard and bring key trending and standard
reports to you all in one place.
Trending, forecasting, and exceptions with athene®
Storage Key Metrics – Summary
To
summarize
•
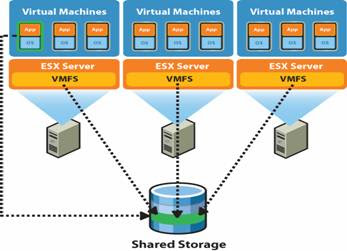
Knowledge of your storage architecture is critical,
you may need to talk to a separate storage team to get this information
•
Define storage occupancy versus performance
•
Discuss space utilization and define
•
Review virtualization and clustering complexities
•
Explore key metrics and their limitations
Identify key report
types and areas that are most important and start with the most critical.
Dale Feiste
Principal Consultant